Electrically controlled ion transport device 2x
Full text: EP 2232260 (A1)
Full text: EP 2232260 (A1)

Full text: EP 2265325 (A1)
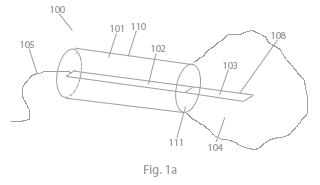
A device for electrically controlled of ions, comprises a first electrolyte; a first electrode, which is arranged in direct or indirect contact with the first electrolyte, an encapsulation; and an ion conductor, which is arranged to receive and/or deliver ions from/to the first electrolyte.
The encapsulation is arranged to effectively enclose the first electrolyte, and the ion conductor is arranged to transport ions from/to an outside of the encapsulation.
Full text: WO 2010119069 (A1)
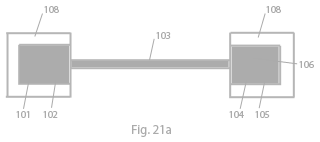
A device for controlled transport of ions is provided comprising an ion source element (100a) and an ion target element (100b) both conducting ions of a first class e.g. cations, and an ion selective element (101) which conducts ions of a second class e.g. anions.
The device further comprises a transport element (102), which receives ions from the ion source element and releases them to the ion target element in response to an electrochemical potential difference provided across the ion transport element. In use a first electrochemical potential is applied to the control element (101), which increases the concentration of ions of said second class, which increased concentration in turn increases the ion transport rate of ions of said first class in the ion transport element (102).
Full text: WO 2011124253 (A2)
The present disclosure relates to a device comprising a conductive substrate surface (19), at least one layer of a conductive polymer (14) deposited on the surface (19), a first electrolyte (13) arranged in contact with the conductive polymer layer, and a counter electrode (11), arranged in contact with the first electrolyte (13), such that a potential difference can be applied between the conductive substrate (15) and the counter electrode (11).
The conductive polymer (14), in a first state, before applying the potential difference, exhibits a first adhesive capacity, wherein the conductive polymer layer (14) is substantially attached to the conductive substrate surface (19). In a second state, subsequent to application of the potential difference, the conductive polymer (14), exhibits a second adhesive capacity, such that at least a portion of the conductive polymer layer (14) is substantially released from the conductive substrate surface (19).